Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.
Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.
Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.
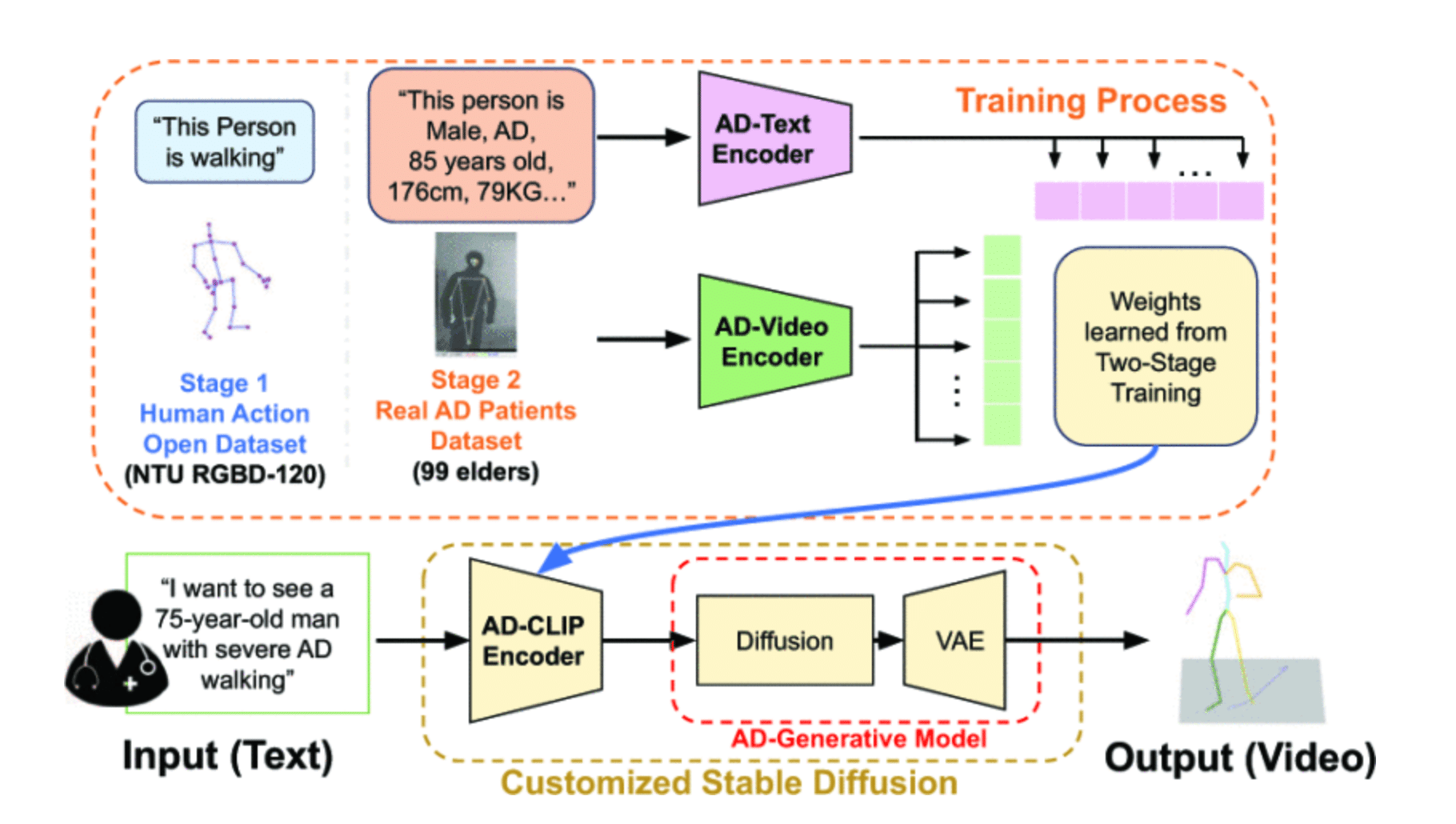
DrHouse introduces a novel diagnostic algorithm that concurrently evaluates potential diseases and their likelihood, facilitating more nuanced and informed medical assessments.
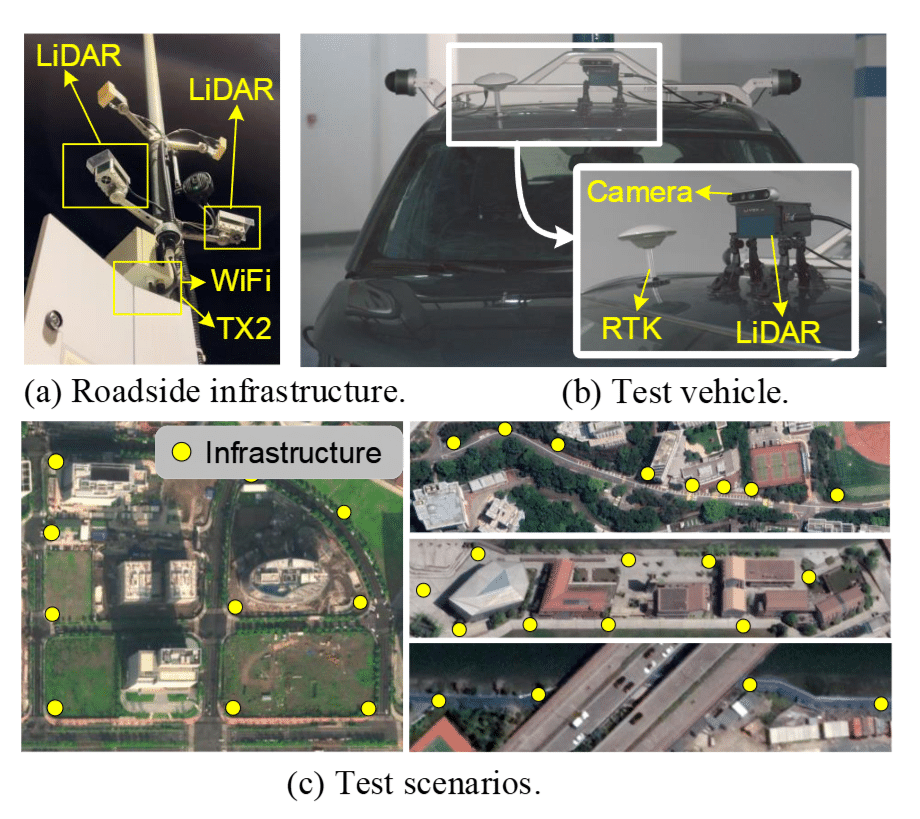
VILAM, a novel framework that leverages intelligent roadside infrastructures to realize high-precision and globally consistent localization and mapping on autonomous vehicles. VILAM utilize the scene measurement from the infrastructure to correct errors in the vehicle map.
ArtFL, a novel federated learning system designed to support dynamic runtime inference through multi-scale training. The key idea of ArtFL is to utilize the data resolution, i.e., frame resolution of videos, as a knob to accommodate dynamic inference latency requirements. Specifically, we initially propose data-utility-based multi-scale training, allowing the trained model to process data of varying resolutions during inference.