SocialMind, the first LLM-based proactive AR social assistive system that provides users with in-situ social assistance. SocialMind employs human-like perception leveraging multi-modal sensors to extract both verbal and nonverbal cues, social factors, and implicit personas, incorporating these social cues into LLM reasoning for social suggestion generation.
Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.
Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.
Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.
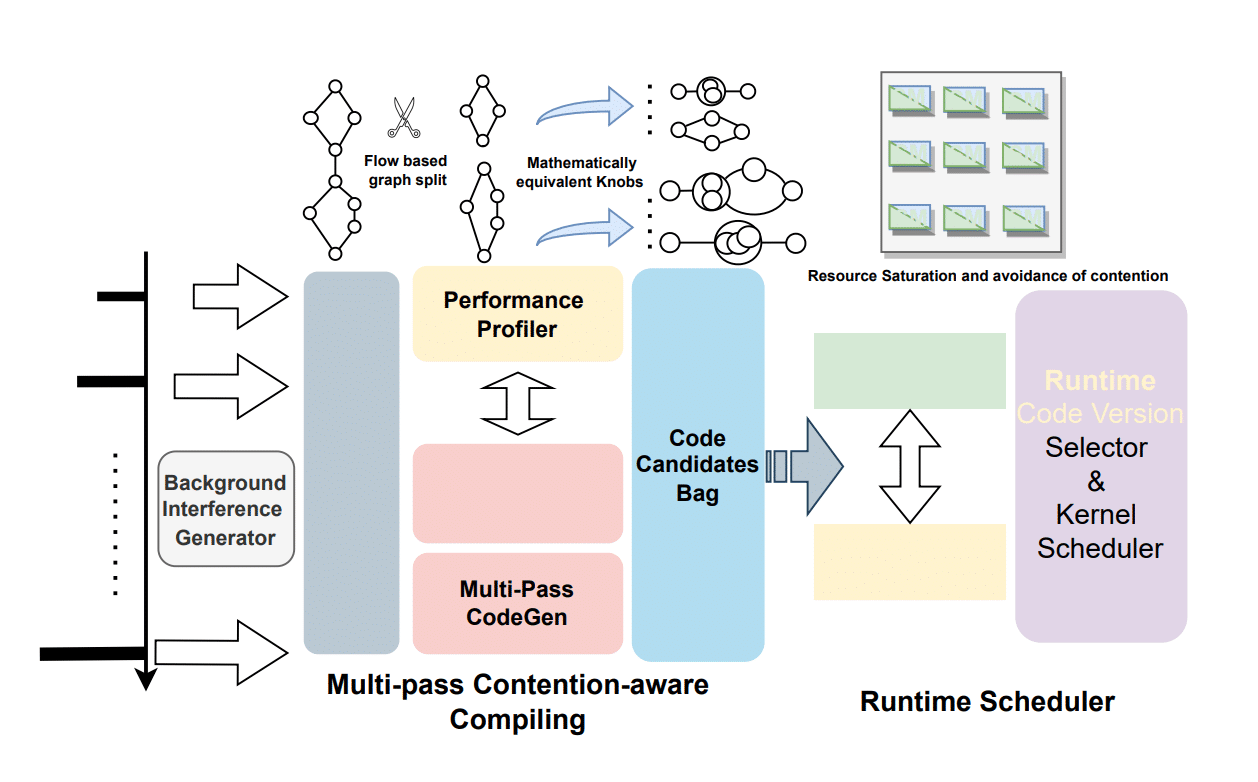
ArtFL, a novel federated learning system designed to support dynamic runtime inference through multi-scale training. The key idea of ArtFL is to utilize the data resolution, i.e., frame resolution of videos, as a knob to accommodate dynamic inference latency requirements. Specifically, we initially propose data-utility-based multi-scale training, allowing the trained model to process data of varying resolutions during inference.
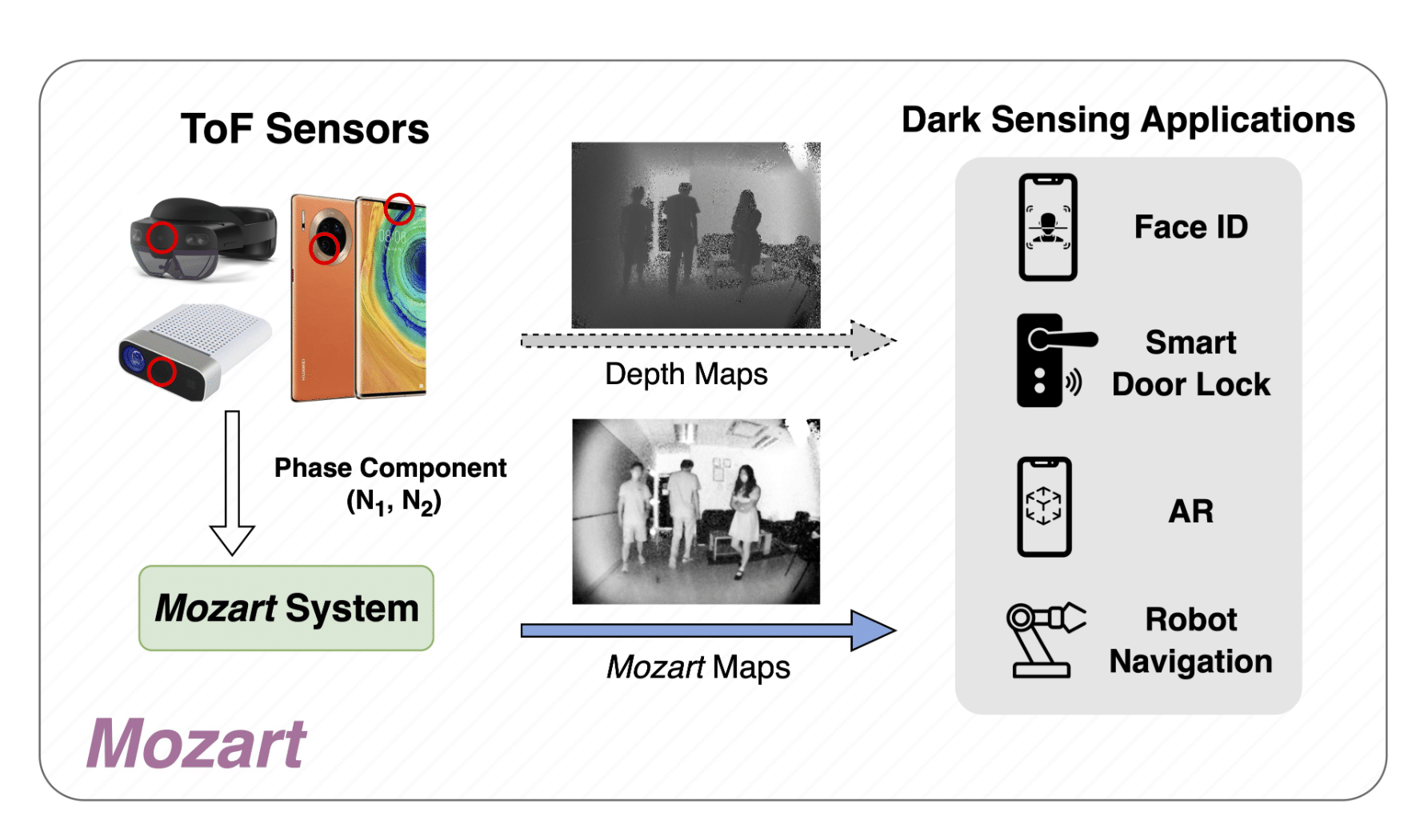
Mozart is a breakthrough mobile sensing system using Time-of-Flight (ToF) cameras to generate high-resolution maps in dark environments. By innovatively manipulating ToF phase components, it enhances texture information. Implemented on Android devices, Mozart operates in real-time, providing a cost-effective, high-performance solution for advanced sensing in the dark.
Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.
Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.
Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.
Argus, a wearable add-on system based
on stripped-down (i.e., compact, lightweight, low-power, limitedcapability) mmWave radars. It is the first to achieve egocentric human mesh reconstruction in a multi-view manner. Compared with
conventional frontal-view mmWave sensing solutions, it addresses
several pain points, such as restricted sensing range, occlusion, and
the multipath effect caused by surroundings.